
|
|
|
Note that we said that an operating system is a set of programs. The
most important program in the operating system, the program that manages the
operating system, is the supervisor program, most of which remains in memory and
is thus referred to as resident. The supervisor controls the entire operating
system and loads into memory other operating system programs (called
nonresident) from disk storage only as needed.
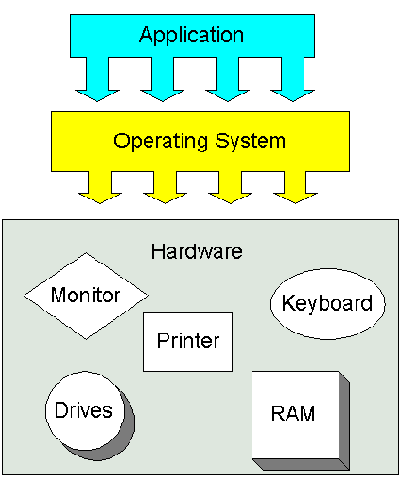
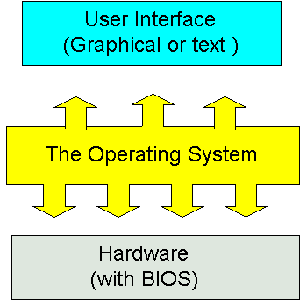
An operating system has
three main functions: (1) manage the computer's resources, such as the central
processing unit, memory, disk drives, and printers, (2) establish a user
interface, and (3) execute and provide services for applications software. Keep
in mind, however, that much of the work of an operating system is hidden from
the user; many necessary tasks are performed behind the scenes. In particular,
the first listed function, managing the computer's resources, is taken care of
without the user being aware of the details. Furthermore, all input and output
operations, although invoked by an applications program, are actually carried
out by the operating system. Although much of the operating system functions are
hidden from view, you will know when you are using an applications software
package, and this requires that you invoke-call into action-the operating
system. Thus you both establish a user interface and execute software.
Operating systems for mainframe and other large computers are even more
complex because they must keep track of several programs from several users all
running in the same time frame. Although some personal computer operating
systems-most often found in business or learning environments-can support
multiple programs and users, most are concerned only with a single user. We
begin by focusing on the interaction between a single user and a personal
computer operating system.
Operating Systems for Personal Computers:
An Overview
If you peruse software offerings at a retail store, you will
generally find the software grouped according to the computer, probably IBM
(that is, IBM compatible) or Macintosh, on which the software can be used. But
the distinction is actually finer than the differences among computers:
Applications software-word processing, spreadsheets, games, whatever-are really
distinguished by the operating system on which the software can run.
Generally, an application program can run on just one operating system.
Just as you cannot place a Nissan engine in a Ford truck, you cannot take a
version of WordPerfect designed to run on an IBM machine and run it on an Apple
Macintosh. The reason is that IBM personal computers and others like them have
Intel-compatible microprocessors and usually use Microsoft's operating system,
called MS-DOS (for Microsoft disk operating system) on older computers, and
Windows95 or Windows98 on more modern computers. Computers that have come out
since the year 2000 often come with Windows ME (Millennium Edition),
Windows2000, or more recently WindowsXP. Macintoshes use an entirely different
operating system, called the
Macintosh operating system, which is produced by Apple. Over 75 percent of
personal computers use a version of Windows as their operating systems.
Macintosh comprises about 15 percent of the market, with other operating systems
such as Linux comprising the rest.
Users do not set out to buy operating
systems; they want computers and the applications software to make them useful.
However, since the operating system determines what software is available for a
given computer, many users observe the high volume of software available for
MS-DOS machines and make their computer purchases accordingly. Others prefer the
user-friendly style of the Macintosh operating system and choose Macs for that
reason.
Although operating systems differ, many of their basic functions
are similar. We will show some of the basic functions of operating systems by
examining MS-DOS.
A Look at MS-DOS
Most users today have a
computer with a hard disk drive. When the computer is turned on, the operating
system will be loaded from the hard drive into the computer's memory, thus
making it available for use. The process of loading the operating system into
memory is called bootstrapping, or booting the system. The word booting is used
because, figuratively speaking, the operating system pulls itself up by its own
bootstraps. When the computer is switched on, a small program (in ROM-read-only
memory) automatically pulls up the basic components of the operating system from
the hard disk. From now on, we will refer to MS-DOS by its commonly used
abbreviated name, DOS, pronounced to rhyme with boss.
The net observable
result of booting DOS is that the characters C> (or possibly C:\>) appear
on the screen. The C refers to the disk drive; the > is a prompt, a signal
that the system is prompting you to do something. At this point you must give
some instruction to the computer. Perhaps all you need to do is key certain
letters to make the application software take the lead. But it could be more
complicated than that because C> is actually a signal for direct
communication between the user and the operating system.
Although the
prompt is the only visible result of booting the system, DOS also provides the
basic software that coordinates the computer's hardware components and a set of
programs that lets you perform the many computer system tasks you need to do. To
execute a given DOS program, a user must issue a command, a name that invokes a
specific DOS program. Whole books have been written about DOS commands, but we
will consider just a few that people use for ordinary activities. Some typical
tasks you can do with DOS commands are prepare (format) new diskettes for use,
list the files on a disk, copy files from one disk to another, and erase files
from a disk.
Microsoft Windows: An Overview
Microsoft Windows
started out as a shell. Windows uses a colorful graphics interface that, among
other things, eases access to the operating system. The feature that makes
Windows so easy to use is a graphical user interface (GUI-pronounced "goo-ee"),
in which users work with on-screen pictures called icons and with menus rather
than with keyed-in. They are called pull-down menus because they appear
to pull down like a window shade from the original selection. Some menus, in
contrast, called pop-up menus originate from a selection on the bottom of the
screen. Furthermore, icons and menus encourage pointing and clicking with a
mouse, an approach that can make computer use both fast and easy.
To
enhance ease of use, Windows is usually set up so that the colorful Windows
display is the first thing a user sees when the computer is turned on. DOS is
still there, under Windows, but a user need never see C> during routine
activities. The user points and clicks among a series of narrowing choices until
arriving at the desired software.
Although the screen presentation and
user interaction are the most visible evidence of change, Windows offers changes
that are even more fundamental. To understand these changes more fully, it is
helpful at this point to make a comparison between traditional operating systems
for large computers and Windows.
In addition to adding a friendly GUI,
Windows operating systems added another important feature to DOS -
multi-tasking. Multi-tasking occurs when the computer has several
programs executing at one time. PCs that ran under DOS could only run one
program at a time. Windows-based computers can have multiple programs (e.g. a
browser, a word processor, and several Instant Messaging instances) running at
the same time. When programs are executing at the same time, they are said to be
executing concurrently.
As we learned, personal computers have only one CPU that handles just one
instruction at a time. Computers using the MS-DOS operating system without a
shell are limited not only to just one user at a time but also to just one
program at a time. If, for example, a user were using a word processing program
to write a financial report and wanted to access some spreadsheet figures, he or
she would have to perform a series of arcane steps: exit the word processing
program, enter and use and then exit the spreadsheet program, and then re-enter
the word processing program to complete the report. This is wasteful in two
ways: (1) the CPU is often idle because only one program is executing at a time,
and (2) the user is required to move inconveniently from program to program.
Multi-tasking allows several programs to be active at the same time,
although at an instant in time the CPU is doing only one instruction for one of
the active programs. The Operating System manages which instructions to send to
the CPU. Since computers are so fast, the operating system can switch the
program that gets to execute on the CPU so quickly, the user can not tell. This
is what allows your computer to be "listening" for incoming instant messages,
for instance, while you use a word processor to write a paper.
How
The Operating System Works
Booting
When the power to a
computer is turned on, the first program that runs is usually a set of
instructions kept in the computer's Read-Only Memory (ROM) that examines the
system hardware to make sure everything is functioning properly. This Power-On
Self Test (POST) checks the CPU, memory, and basic input-output systems for
errors and stores the result in a special memory location. Once the POST has
successfully completed, the software loaded in ROM (sometimes called firmware)
will begin to activate the computer's disk drives. In most modern computers,
when the computer activates the hard disk drive, it finds the first piece of the
operating system, the bootstrap loader.
The bootstrap loader is a small program that has a single function: It loads the operating system into memory and allows it to begin operation. In the most basic form, the bootstrap loader sets up the small driver programs that interface with and control the various hardware sub-systems of the computer. It sets up the divisions of memory that hold the operating system, user information and applications. It establishes the data structures that will hold the myriad signals, flags and semaphores that are used to communicate within and between the sub-systems and applications of the computer. Finally it turns control of the computer over to the operating system.
The operating system's tasks, in the most general sense, fall into six categories:
Processor Management
The heart of managing the processor comes down
to two related issues: First, ensuring that each process and application
receives enough of the processor's time to function properly and, second, using
as many processor cycles for real work as is possible. The basic unit of
software that the operating system deals with in scheduling the work done by the
processor is either a process or a thread, depending on the
operating system.
It's tempting to think of a process as an application, but that gives an incomplete picture of how processes relate to the operating system and hardware. The application you see (word processor or spreadsheet or game) is, indeed, a process, but that application may cause several other processes to begin, for tasks like communications with other devices or other computers. There are also numerous processes that run without giving you direct evidence that they ever exist. A process, then, is software that performs some action and can be controlled -- by a user, by other applications or by the operating system.
It is processes, rather than applications, that the operating system controls and schedules for execution by the CPU. In a single-tasking system, the schedule is straightforward. The operating system allows the application to begin running, suspending the execution only long enough to deal with interrupts and user input. Interrupts are special signals sent by hardware or software to the CPU. It's as if some part of the computer suddenly raised its hand to ask for the CPU's attention in a lively meeting. Sometimes the operating system will schedule the priority of processes so that interrupts are masked, that is, the operating system will ignore the interrupts from some sources so that a particular job can be finished as quickly as possible. There are some interrupts (such as those from error conditions or problems with memory) that are so important that they can't be ignored. These non-maskable interrupts (NMIs) must be dealt with immediately, regardless of the other tasks at hand.
While interrupts add some complication to the execution of processes in a single-tasking system, the job of the operating system becomes much more complicated in a multi-tasking system. Now, the operating system must arrange the execution of applications so that you believe that there are several things happening at once. This is complicated because the CPU can only do one thing at a time. In order to give the appearance of lots of things happening at the same time, the operating system has to switch between different processes thousands of times a second. Here's how it happens. A process occupies a certain amount of RAM. In addition, the process will make use of registers, stacks and queues within the CPU and operating system memory space. When two processes are multi-tasking, the operating system will allow a certain number of CPU execution cycles to one program. After that number of cycles, the operating system will make copies of all the registers, stacks and queues used by the processes, and note the point at which the process paused in its execution. It will then load all the registers, stacks and queues used by the second process and allow it a certain number of CPU cycles. When those are complete, it makes copies of all the registers, stacks and queues used by the second program, and loads the first program.
All of the information needed to keep track of a process when switching is kept in a data package called a process control block. The process control block typically contains an ID number that identifies the process, pointers to the locations in the program and its data where processing last occurred, register contents, states of various flags and switches, pointers to the upper and lower bounds of the memory required for the process, a list of files opened by the process, the priority of the process, and the status of all I/O devices needed by the process. When the status of the process changes, from pending to active, for example, or from suspended to running, the information in the process control block must be used like the data in any other program to direct execution of the task-switching portion of the operating system.
This process swapping happens without direct user interference, and each process will get enough CPU time to accomplish its task in a reasonable amount of time. Trouble can come, though, if the user tries to have too many processes functioning at the same time. The operating system itself requires some CPU cycles to perform the saving and swapping of all the registers, queues and stacks of the application processes. If enough processes are started, and if the operating system hasn't been carefully designed, the system can begin to use the vast majority of its available CPU cycles to swap between processes rather than run processes. When this happens, it's called thrashing, and it usually requires some sort of direct user intervention to stop processes and bring order back to the system.
One way that operating system designers reduce the chance of thrashing is to reduce the need for new processes to perform various tasks. Some operating systems allow for a "process-lite," called a thread that can deal with all the CPU-intensive work of a normal process, but generally does not deal with the various types of I/O, and does not establish structures requiring the extensive process control block of a regular process. Finally, a process may start many threads or other processes, but a thread cannot start a process.
So far, all the scheduling we've discussed has concerned a single CPU. In a
system with two or more CPUs, the operating system must divide the workload
among the CPUs, trying to balance the demands of the required processes with the
available cycles on the different CPUs. Some operating systems (called
asymmetric) will use one CPU for their own needs, dividing application processes
among the remaining CPUs. Other operating systems (called symmetric) will divide
themselves among the various CPUs, balancing demand versus CPU availability even
when the operating system itself is all that's running. Even if the operating
system is the only software with execution needs, the CPU is not the only
resource to be scheduled. Memory management is the next crucial step in making
sure that all processes run smoothly.
Memory and Storage
Management
When an operating system manages the computer's memory, there
are two broad tasks to be accomplished. First, each process must have enough
memory in which to execute, and it can neither run into the memory space of
another process, nor be run into by another process. Next, the different types
of memory in the system must be used properly, so that each process can run most
effectively. The first task requires the operating system to set up memory
boundaries for types of software, and for individual applications.
As an example, let's look at an imaginary system with 1 megabyte of RAM. During the boot process, the operating system of our imaginary computer is designed to go to the top of available memory and then "back up" far enough to meet the needs of the operating system itself. Let's say that the operating system needs 300 kilobytes to run. Now, the operating system goes to the bottom of the pool of RAM, and starts building up with the various driver software required to control the hardware subsystems of the computer. In our imaginary computer, the drivers take up 200 kilobytes. Now, after getting the operating system completely loaded, there are 500 kilobytes remaining for application processes.
When applications begin to be loaded into memory, they are loaded in block sizes determined by the operating system. If the block size is 2 kilobytes, then every process that is loaded will be given a chunk of memory that is a multiple of 2 kilobytes in size. Applications will be loaded in these fixed block sizes, with the blocks starting and ending on boundaries established by words of 4 or 8 bytes. These blocks and boundaries help to ensure that applications won't be loaded on top of one another's space by a poorly calculated bit or two. With that ensured, the larger question is what to do when the 500 kilobyte application space is filled.
In most computers it's possible to add memory beyond the original capacity. For example, you might expand RAM from 1 to 2 megabytes. This works fine, but tends to be relatively expensive. It also ignores a fundamental fact of life -- most of the information that an application stores in memory is not being used at any given moment. A processor can only access memory one location at a time, so the vast majority of RAM is unused at any moment. Since disk space is cheap compared to RAM, then moving information in RAM to hard disk intelligently can greatly expand RAM space at no cost. This technique is called Virtual Memory Management.
Disk storage is only one of the memory types that must be managed by the operating system, and is the slowest. Ranked in order of speed, the memory in a computer system is:
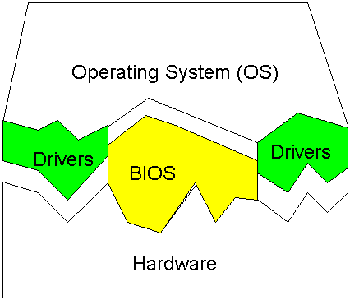
Because there are such wide differences in the hardware controlled through drivers, there are differences in the way that the driver programs function, but most are run when the device is required, and function much the same as any other process. The operating system will frequently assign high priorities blocks to drivers so that the hardware resource can be released and readied for further use as quickly as possible.
One reason that drivers are separate from the operating system is so that new functions can be added to the driver-and thus to the hardware subsystems-without requiring the operating system itself to be modified, recompiled and redistributed. Through the development of new hardware device drivers, development often performed or paid for by the manufacturer of the subsystems rather than the publisher of the operating system, input/output capabilities of the overall system can be greatly enhanced.
Managing input and output is largely a matter of managing queues and buffers, special storage facilities that take a stream of bits from a device, from keyboards to serial communications ports, holding the bits, and releasing them to the CPU at a rate slow enough for the CPU to cope with. This function is especially important when a number of processes are running and taking up processor time. The operating system will instruct a buffer to continue taking input from the device, but to stop sending data to the CPU while the process using the input is suspended. Then, when the process needing input is made active once again, the operating system will command the buffer to send data. This process allows a keyboard or a modem to deal with external users or computers at a high speed even though there are times when the CPU can't use input from those sources.
Managing all the resource of the computer system is a large part of the operating system's function and, in the case of real-time operating systems, may be virtually all the functionality required. For other operating systems, though, providing a relatively simple, consistent way for applications and humans to use the power of the hardware is a crucial part of their reason for existing.
The continuing growth of the Internet and the proliferation of computers
that aren't standard desktop or laptop machines means that operating systems
will change to keep pace, but the core management and interface functions will
continue, even as they evolve.